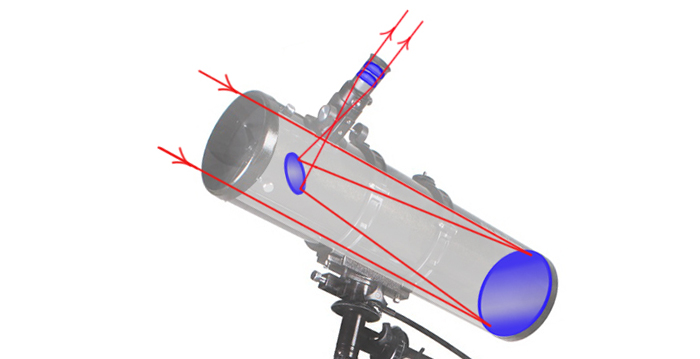
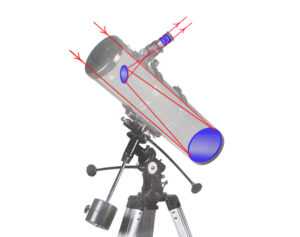
In 59 years after Galileo`s discovery, Isaac Newton designed the first reflecting telescope, based on the scheme of Scottish astronomer James Gregory (his book “Optica Promota”, 1663 year). A reflector uses a mirror instead of lenses to gather light. After the hit in an objective, a beam of light goes to the opposite mirror and turns back to the eyepiece.
Types of reflecting telescopes and how do they work
There are several most famous reflecting telescope designs:
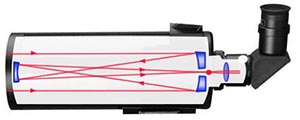
Cassegrain. The main big mirror is concave or parabolic. It transfers light to a small convex secondary mirror. The system suffers from a coma.
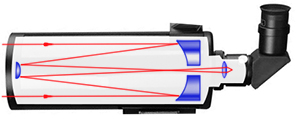
Gregorian, which uses the concave parabolic main mirror and another one – small, concave elliptic. An eyepiece is built in the back of the pipe.
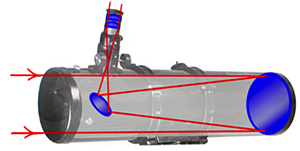
Newtonian. The secondary flat mirror is located near the focus point. As it`s turned diagonal, it leads the light outside. This type has a recognizable design, where the eyepiece sticks out of a pipe side.
Ritchey-Chrétien. An updated Cassegrain system. The main mirror is hyperbolic.

Nesmith. A secondary mirror is mounted on stretch marks, hence there are radial distortions.
The Newtonian scheme remains the most popular among reflecting telescopes.
Advantages of Reflecting telescopes:
- Powerful reflectors are cheaper than two other types
- Good for the deep sky (big aperture makes dim objects available)
- They are compact (a mirrors system allows the long focal length to be fitted into the short case)
- They give bright image without chromatic aberrations
Disadvantages of reflecting telescopes:
- Low contrast image
- The open design of a case causes hit of dust and dirt on mirrors
- Need in a long time for temperature stabilization
- Need in an adjustment time to time