Good afternoon, dear readers! Today let's talk about magnification of binoculars. Undoubtedly, magnification is one of the most important characteristics of any optical device, which we certainly pay attention to when choosing one. At first glance it may seem that the question of choosing magnification is not worth an egg: the bigger, the better. But everything is not so simple. And it's not even just about the distance to the observed object. The magnification of binoculars also affects the quality of the image and the ability to observe at dusk. How is it connected? Let's find out.
Magnification explained
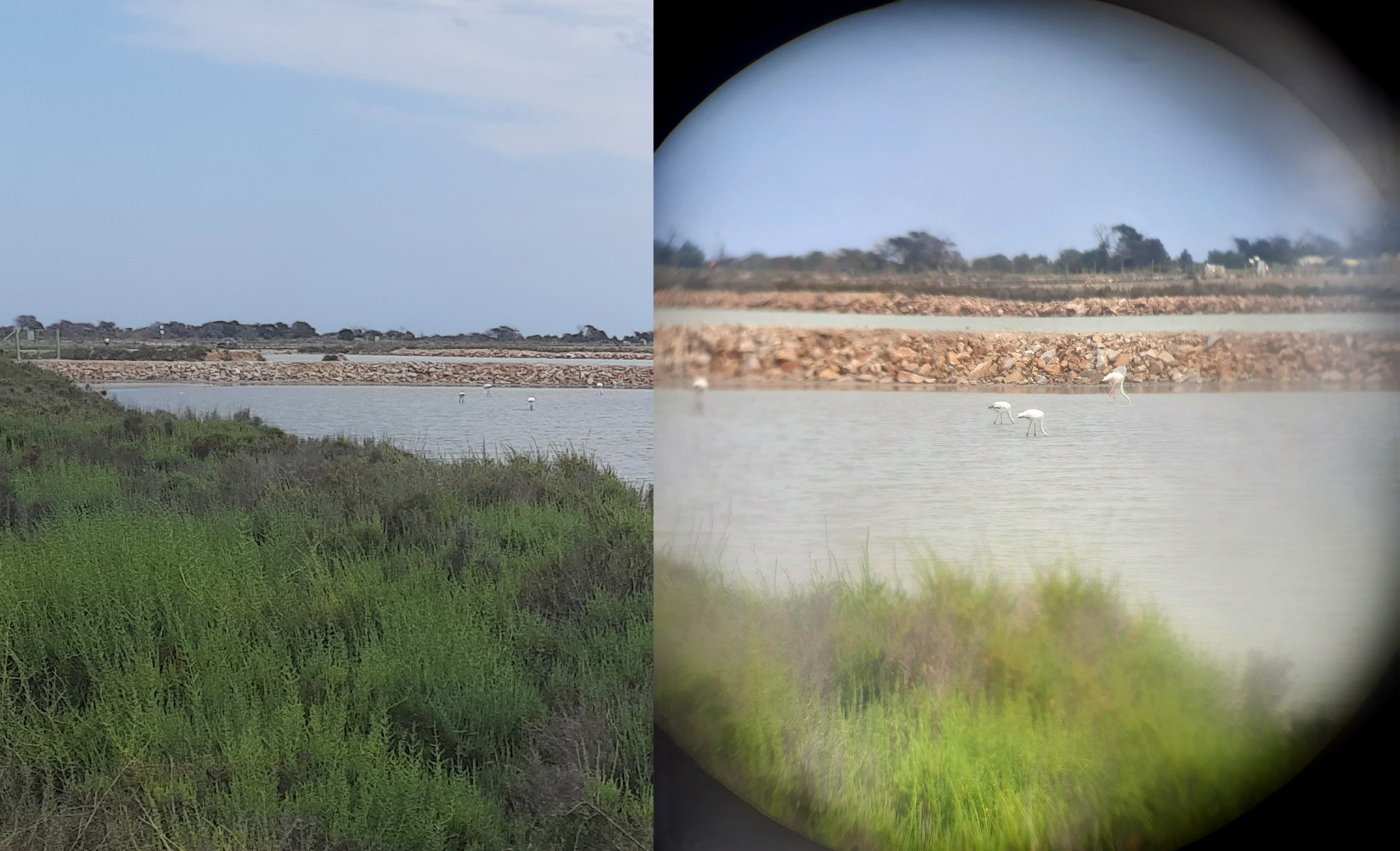
So, what is binocular magnification? It's how many times the instrument brings the object you're looking at closer. That is, if the magnification of your binoculars is eight, you will see the object as if it were eight times closer to you.
Depending on the strength of the magnification, binoculars are differentiated by power. A magnification of 2-5x is considered small, 5-10x is considered medium, and 10 and above is considered large.
In addition, there are binoculars with fixed and variable magnification.
So why does bigger not mean better?
- The higher the magnification, the smaller the angle of view.
- The higher the magnification, the harder it is to keep the image in your field of view.
- The higher the magnification, the lower the luminosity, which means less brightness and the ability to see details in low light.
Can binoculars zoom in and out?
Yes, some binoculars can zoom in and out on objects. This type of magnification is called variable magnification. You can recognize them by the lever on the body, which is usually located near the eyepiece. It allows you to change the magnification.
Zoom-binoculars are more complex than models with fixed magnification, and the mechanism for switching the magnification is often their weak point. Users often report breakages. In addition, there is a fairly common problem with the two optical tubes of such binoculars having different magnifications. After all, when the magnification can change, it should change synchronously. And it is difficult to achieve this. Sometimes the difference is almost imperceptible, and sometimes it is significant. Be careful when buying, especially carefully check inexpensive models.
Nevertheless, pancreatic binoculars also find their application. For example, they are good in situations where high image clarity is not necessary, but you need to quickly examine the object in detail. This can be sports matches, search operations.
How to Read Binocular Magnification
The magnification value is always indicated on the body of the binoculars together with the diameter of the objective lenses. The first is the magnification, the second is the diameter of the lenses. For example, 8×40 is a very common combination of parameters in binoculars for general purpose.
How does magnification work? Deep in specs
The magnification power of binoculars depends on two characteristics: the focal length of the objective lens and the focal length of the eyepiece. The longer the focal length of the objective lens, the higher the magnification of the binoculars. And the smaller the focal length of the eyepiece, the higher the magnification of the binoculars. Magnification can be calculated using the formula:
Magnification = Focal length of the objective lens /Focal length of the eyepiece
For example, if the focal length of the objective lens is 200mm and the focal length of the eyepiece is 20mm, the magnification will be 10x.
Focal length is the distance from the center of a lens (or lens system) to the point at which parallel rays of light are collected (the focal plane). Long focal length lenses can make the design more bulky, so binoculars with high magnification (from 12-15) are larger than normal binoculars.
As for eyepieces, there's a downside here, too. As we said, the smaller the focal length of the eyepiece, the higher the magnification. At the same time, eyepieces with a small focal length can reduce the field of view and depth of field of the image. So, balance is important here too.
Let's take a look at what other features play a role when choosing binoculars with this or that magnification.
Binocular’s magnification and Twilight factor
While we are delving into technical specifications, let us also mention the fact that the magnification of binoculars has a direct impact on the brightness of the image. Roughly speaking, the higher the magnification, the lower the brightness and the lower the ability of the binoculars to distinguish details of an object at dusk. This ability is expressed by the twilight factor, which is calculated using the formula:
The square root of the product of (Magnification * Lens Diameter)
For example, if we have binoculars 8×42, the calculation is as follows:
8*42 = 336
√336 = 18.3
For observation in binoculars at late hours, the twilight factor of the instrument should be at least 17. Our binoculars will do.
Exit pupil and binocular's magnification
Well, since we are such enthusiasts, let's dive a little deeper. In optical engineering, there is such a thing as exit pupil. It is the width of the light beam that passes through the eyepiece and enters the observer's eye. This is an important parameter, and – yes, dear friends! – magnification affects it too. It is calculated by the formula:
Exit pupil = Lens diameter / Magnification
For example, for 6×40 binoculars the exit pupil diameter will be 6.6 mm.
What does the exit pupil affect? The brightness of the image. How? The human eye also has an exit pupil, and its diameter varies from 2 to 8 mm depending on the light. If the width of the exit pupil of binoculars is smaller than the width of the human pupil, then too little light will enter the eye and the image will be dark. Such binoculars are suitable only for daytime observations. For observation at dusk, the diameter of the exit pupil of the binoculars should be 5-7 mm.
Magnification and Field of view
The linear field of view of an optical instrument means the distance between two extreme points visible through the instrument and located at a distance of 1000 meters from it. And, as you may have already guessed, it is also affected by magnification, or, to be more precise, by the focal length of lenses (which affects magnification). In order not to scare you and not to confuse you at all, let's put it simply: the longer the focal length of the lens, the narrower the field of view. But it should be noted that it's not the only thing that has an impact. What else?
- For example, if the binoculars have special wide-angle eyepieces, the field of view will be wide even at high magnification.
- Also, the type of prisms has an influence: Porro prisms give a wider field of view.
- And the width of the objective lens and exit pupil indirectly influence: the wider they are, the brighter the image at the edges of the field of view, which also increases it visually.
Examples:
10×50 binoculars can have a field of view of about 100 meters at 1000 meters, and 8×40 – up to 130-140 meters.
You may also see angular field of view rather than linear field of view in the specifications. Under the visible angular field is the angle between the two lines connecting the pupil of the observer's eye and the two extreme points of visible space. Essentially describes the same parameter of binoculars, but is calculated in degrees. To understand, optical devices with an apparent field of view of more than 60 degrees are considered wide-angle.
Below is a table with approximate values of the linear field of view of binoculars depending on its magnification and angular field of view.
| x\° | 50° | 55° | 60° | 65° | 70° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6x | 145 | 160 | 175 | 189 | 204 |
| 7x | 125 | 137 | 150 | 162 | 175 |
| 8x | 109 | 120 | 131 | 142 | 153 |
| 10x | 87 | 96 | 105 | 113 | 122 |
| 12x | 73 | 80 | 87 | 95 | 102 |
| 16x | 55 | 60 | 65 | 71 | 76 |
| 20x | 44 | 48 | 52 | 57 | 61 |
How far can binoculars zoom? Comparison chart
As we have discussed above, the magnification of binoculars affects not only the size of the visible object at a certain distance, but also the quality of the picture and the apparent field of view. Therefore, depending on how you are going to use the binoculars, it is recommended to choose different magnification. The magnification distance of most binoculars is from 4 to 10 km. There are also more special models whose focusing distance is very small or, on the contrary, very large. For example, theater binoculars have a minimum focusing distance of only 3 meters. At the same time, they are characterized by a small magnification – only 4-5 times. On the other hand, there are astronomical binoculars with a magnification of 15-20x, which work at a distance of 80 meters and more.
You can see the approximate ratio of multiplicity and range in the table below. We have an article answering the question in more detail How far can binoculars see, we recommend reading it.
| Binocular Specification | Ideal Application | Maximum Effective Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 8×32 | Birdwatching, hiking | ~2-3 km |
| 10×42 | Wildlife watching, hunting | ~4-5 km |
| 10×50 | Celestial observations, long-range viewing | ~5-6 km |
| 20×80 | Astronomical observations, professional use | ~15-20 km |
Next, we'll take a closer look at the popular Bushnell and Nikon binocular models.
Nikon binoculars zoom chart
Best binoculars magnification for your activity
There are more or less universal binoculars that can be used for a variety of purposes: hunting, fishing, watching sporting events, observing the moon. These are small and light binoculars with magnification from 6 to 10x and lenses with a diameter from 32 to 50 mm. Let's take a closer look at what zoom is better to choose depending on your tasks.
What zoom is better for hunting and safari?
For hunting it is recommended to choose binoculars with magnification from 8 to 10x. This magnification allows you to observe animals from a fairly long distance, while the focal length is not very long, so the binoculars are quite compact and lightweight. The optimal diameter of the lenses is 35-40 mm. This combination of parameters will provide a bright image and a wide field of view.
Bird watching
Binoculars for bird watching are close to hunting binoculars. But here image quality and brightness are more important, as well as a wide field of view to look for birds at a distance. We can recommend magnification from 8 to 10 and lenses from 40 mm and more. ED optics are desirable. A magnification of 12x is also suitable, but you need a tripod and readiness for stationary observations. For twilight observations you need high brightness – look for binoculars with a twilight factor of 17 or more.
Whale watching
In general, the recommendations here are the same as for hunting or bird watching. Tourist ships should be kept at a safe distance, as whales, due to their size, can overturn the ship. Therefore, it is better to use binoculars with magnification of 8-10x to observe them. It does not make sense to take more, as it will be impossible to keep the image in the field of view under rocking conditions. Don't forget that binoculars should have at least minimal protection against water.
Paddling, boating, yahting
For kayaking and yachting the recommendations are about the same as for hunting: low magnification of 6-8x, larger lenses for a wide field of view and brightness. It is also recommended that the binoculars have anti-fogging and water protection.
Bagpacking and hiking
For hiking you should choose compact and lightweight binoculars with an average magnification of 6–10x and large objective lenses for bright images at dusk and a wide field of view. It's also important to protect the body from splashes, dust and temperature extremes.
Sport events and concerts
For viewing sporting events or concerts in stadiums, it is the field of view, not the magnification, that is important as the object is at a short distance. It is recommended to choose a field of view from 120 meters and wider at a distance of 1000 meters. It is also important that the binoculars are lightweight and have good covered optics.
Stargazing
Binoculars are often used for initial astronomical observations. For observations of the Moon, even 8-10x magnification will suffice. And for more distant and dim objects one buys professional astronomical binoculars with magnification of 18-25x. Observation is carried out with a tripod. It is important to realize when choosing binoculars for astronomy that the diameter of the lenses is probably even more important than the magnification, as the observation of space objects requires high luminosity. It is recommended to focus on the exit pupil diameter of 3.5 mm and above. Thus, if the lenses are small (40-50 mm), for astronomical observations it is better to choose a magnification of no more than 10-12x.
Compact zoom binoculars
A separate very popular group of binoculars are compact binoculars with high magnification or variable magnification. These are models such as 8×24, 12×32, 6-15×21, etc. Such binoculars will have a very narrow field of view and the ability to observe only during the day. Their advantage is their compactness and light weight, it is convenient to take them with you on the road. Such binoculars can be recommended for spot observations: for inspection of city objects, for sightseeing tours.
Are zoom binoculars any good for astronomy?
Continuing with the topic of pancreatic binoculars, let's touch on the topic of astronomy. Many astro-lovers think about buying zoom binoculars, as variable magnification gives a lot of possibilities. It seems that such binoculars are like several binoculars in one. But the answer to the question is more of a no than a yes.
Despite the fact that there are some successful models, more often you can hear about negative experiences of using binoculars with variable magnification for astronomy. In most cases they are caused by a very narrow field of view at maximum magnification and low luminosity. For comfortable astronomical observations, a combination of small magnification and large lenses is recommended. For example, 12×50, 14×50, 10×40. The exit pupil width should be about 4 mm for observing extended objects, 1.5 for observing stars, 0.6 for planets. Here's what to look for when choosing astronomical binoculars.
If the maximum magnification of the pancreatic binoculars you want to take is about 15x and the lenses are at least 40mm, you can try. But if the magnification is higher and the lenses are smaller, I don't recommend it. Pancreatic binoculars of such famous brands as Celestron, Nikon, created specifically for space observation, of course suitable and recommended for purchase. But they do not cost cheap. In other cases – it is a risk. It is also worth taking into account that pancreatic binoculars have a complex design, and in inexpensive models the magnification switching tool often fails.
Are big zoom binoculars worth it?
Based on all of the above, we can answer unequivocally that binoculars with a large zoom are recommended for purchase if you know exactly why you need such a large magnification. If you realize that you don't need a wide field of view and observations at dusk, but you need to see an object at a very large distance, then yes, binoculars with a large zoom are definitely worth it. In all other cases, we recommend choosing a medium magnification (7-10x) and larger large objective lenses (35-40mm). Read more about how to choose binoculars for your tasks in our other article. Thank you for spending time with us!